A Canonical Tag is placed on a webpage when it contains text that is copied from, or too similar to the text of another webpage.
This is done to show search engines what the preferred version of the page is for ranking, so that the desired landing page appears in search without a duplicate content penalty.
Multiple pages can be canonicalized to the same landing page, which often happens in instances of analytics tracking where URL parameters are added to different campaign type landing pages, all of which but the one intended for Google search being labeled noindex & canonicalized to the original version of the page content.
How Canonical Tags Work
URL A & URL B below both have the same content, which will be problematic in search as it will result in a duplicate content penalty.
Since URL A is more concise & does not contain the parameter in the URL that B Does (“?loc=US”), the webmasters select it as the version that they want to perform in organic search.
A canonical tag is placed on URL B that says link rel=”canonical” href=”https://lg.com/smartphones”/>.
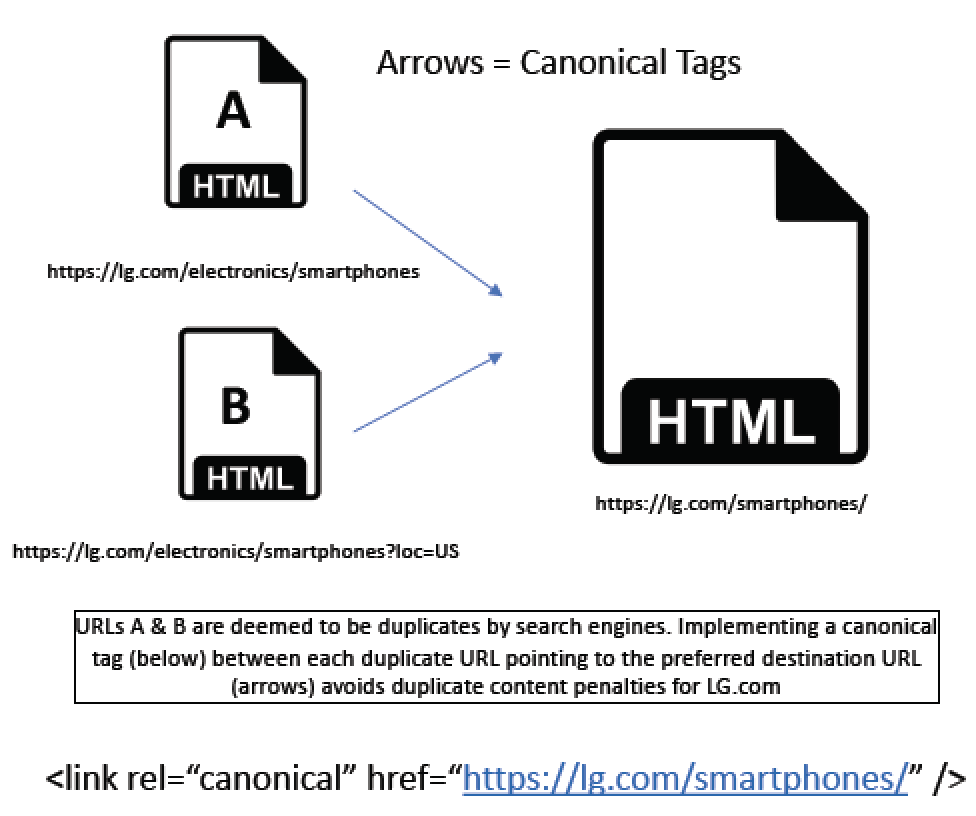
This tells bots to use the “/smartphones/” version of the page in organic search.
Webmasters should also be sure to add in “noindex” tags, as well as update their XML Sitemap & Robots.txt file to reflect that the “/smartphones?loc=US” should not appear in search.